Introduction
Phosphorus (P) is a macronutrient and is required in relatively large amounts for the growth of plants. Phosphorus, in the form of ATP, acts as a battery and gives the plant the energy it needs to perform chemical reactions. Using the energy ATP provides, plants are able to complete the process of photosynthesis to make. Phosphorus is necessary in plants for formation and growth of new cells and the transfer of genetic information from one cell to another (International Plant Nutrition Institute, 1998). Without a sufficient amount of phosphorus, the surface area and number of leaves on a plant are greatly reduced, as well as the growth of shoots and roots. (International Plant Nutrition Institute, 1998). It also limits plants’ abilities to use carbohydrates, which means that as carbohydrates continue to be produced during photosynthesis, they build in the plant instead of being used.
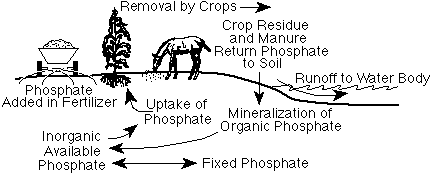 The
phosphorus cycle- how phosphorus is moved throughout ecosystems (picture from
University of Minnesota)
The
phosphorus cycle- how phosphorus is moved throughout ecosystems (picture from
University of Minnesota)
Water in soil usually doesn't contain very much phosphorus, because
phosphorus is not water soluable. Runoff water also helps wash phosphorus
throughout a site, preventing it from building up in high concentrations.
Natural sources of phosphorus are dead organisms decaying,and animal waste
products. Another, less natural, source is runoff from fertilizers in gardens
and farms. (University of Minnesota, 2002)
It is possible for anyone to conduct an experiment like ours because, if you test for water moisture levels, at the same time you can test for phosphorus. As the water flows through a stream, it moves phosphorus through the soil. As you can see, the two relates to one another.