Quick
Facts
What is
photosynthesis?
When you get hungry, you can make yourself a peanut butter and jelly
sandwich. First you need two slices of bread, then peanut butter,
jelly, and any other ingredients you like in your sandwich. After you finish
eating your sandwich, it gives you energy to fuel you through your day.
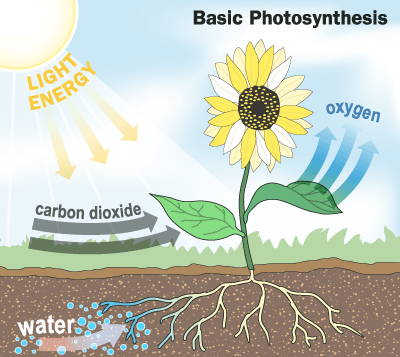
In this same way, plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, water, and nutrients in the soil to make their food!
- Photosynthesis is the process where plants (or algae) convert light energy from the sun, carbon dioxide in the air, water, and nutrients in their surrounding environment to make sugar.
- Sunlight and carbon dioxide enter the plant through its leaves. Inside the leaves are little energy factories (chloroplasts) where photosynthesis occurs. Chloroplasts use the chemical chlorophyll to help them in the process of photosynthesis.
What is chlorophyll? What role does it play in photosynthesis?
Have you ever wondered why plants are green?
Well, it's all because of the chemical chlorophyll!
- Chlorophyll causes the green pigment, or color, in plants.
- But chlorophyll's most important job is to help chloroplasts in the process of photosynthesis
- Chlorophyll molecules are composed of 5 elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and magnesium
- Chlorophyll, with the help of iron (Fe), enables plants to manufacture carbohydrates, which can then in turn help fuel the plant
What is iron (Fe)?
Did you know, Iron Man was actually Fe-male?

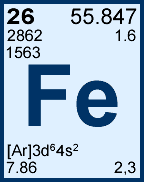
- Iron can also be represented by the symbol "Fe" from the Periodic Table of Elements
- Iron is one of the cheapest and therefore most used metals
- Iron is fourth in abundance among elements, behind oxygen, silicon, and aluminum
- Iron is particularly prevalent in the Earth's core and can also be found in the Earth's crust.
- Iron can be found in many different places, such as rocks, minerals, the human body, green vegetables, and fruit. Iron can even be found in outer space, such as meteorites or stars!
- Iron reacts with different acids and compounds. Have you wondered how rust happens? Well, it's all because iron or steel (a product of melted iron and manganese that has undergone various chemical reactions) came in contact with water and oxygen which causes an oxidation reaction.
How does iron interact in
the environment, specifically with plants?
- The two most common forms of iron are ferrous (Fe+2) or ferric (Fe+3) . Ferrous iron is more soluble and therefore plants use it more than ferric iron.
- Ferrous iron (Fe+2) is more prevalent in acidic soil and reduced environments, such as lowland and waterlogged locations.
-Iron is an essential element in plant growh because it has an active role in the formation of chlorophyll, which in turn, enables the photosynthesis process to occur.
- Iron helps plants to absorb manganese.
What is manganese (Mn)?
Pictured below is a rhodochrosite crystal, named "The
Alma Queen". It is one of the most famous specimens in all of mineralogy!

- Manganese is the fifth most abundant metal in the Earth's crust
- There are over 300 minerals that contain the element Manganese! Some of these minerals include: manganite, Franklinite, rhodochrosite (featured in the image above), and senaite.
- Manganese is repreented with the symbol "Mn" on the Periodic Table of Elements
- Manganese has six different oxidation states:
- Combined with iron, manganese forms the alloy steel. Manganese can also be used as ore in plant fertilizers, animal feed, and colorants for bricks.
- Manganese's name comes from the Greek word for "magic".
How does manganese interact in the environment, specifically with plants?
- Higher levels of iron and moisture in soils determine the rate of manganese absorbtion in plants and also what forms of manganese are available or unavailable to the plants.
- Manganese transports electrons during photosynthesis.
- Manganese splits water molecules to create oxygen molecules during the photophosphorylation process.
- A sign of manganese deficiency is yellowing of a plant’s leaves and tissue.
For even more information, see our references on the Bibliography page!